- English
- Español
- Português
- русский
- Français
- 日本語
- Deutsch
- tiếng Việt
- Italiano
- Nederlands
- ภาษาไทย
- Polski
- 한국어
- Svenska
- magyar
- Malay
- বাংলা ভাষার
- Dansk
- Suomi
- हिन्दी
- Pilipino
- Türkçe
- Gaeilge
- العربية
- Indonesia
- Norsk
- تمل
- český
- ελληνικά
- український
- Javanese
- فارسی
- தமிழ்
- తెలుగు
- नेपाली
- Burmese
- български
- ລາວ
- Latine
- Қазақша
- Euskal
- Azərbaycan
- Slovenský jazyk
- Македонски
- Lietuvos
- Eesti Keel
- Română
- Slovenski
- मराठी
- Srpski језик
How Can Floor Drains Improve Sanitation and Water Management in Residential and Commercial Spaces?
2025-12-16
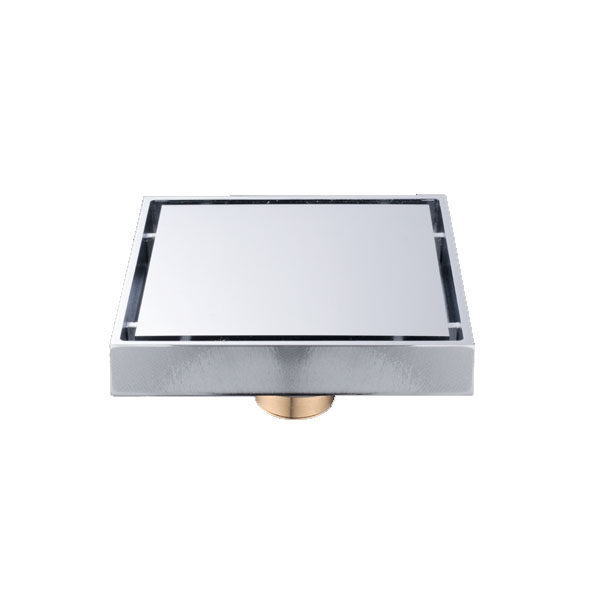
Floor drains are critical components in both residential and commercial plumbing systems, designed to manage excess water, prevent flooding, and maintain hygiene. These systems are installed in bathrooms, kitchens, basements, industrial facilities, and other areas prone to water accumulation. Properly designed and installed floor drains help streamline water drainage, reduce moisture-related damage, and contribute to a safer and cleaner environment. Understanding the specifications, material choices, and installation standards of floor drains is essential for anyone looking to improve water management and sanitation.
Floor drains are available in a variety of materials, including stainless steel, PVC, and cast iron. They feature multiple design elements such as removable grates, trap seals, and anti-odor mechanisms to enhance functionality. Modern floor drains must meet high standards of durability, corrosion resistance, and load-bearing capacity to ensure long-term performance in both commercial and residential applications.
The following table provides a detailed overview of typical floor drain specifications:
| Parameter | Specification Example |
|---|---|
| Material | Stainless Steel 304 / PVC |
| Diameter | 50mm, 75mm, 100mm |
| Height Adjustment Range | 50–150mm |
| Load Rating | Class B (Residential), Class D (Industrial) |
| Trap Type | P-Trap / Deep Seal Trap |
| Surface Finish | Polished, Brushed, Matte |
| Anti-Odor Feature | Yes, with removable silicone seal |
| Installation Type | Floor-mounted, recessed, or adjustable |
This overview demonstrates that floor drains are engineered for both functional efficiency and long-term reliability. Selection of the appropriate material and design depends on the application environment and expected water flow. For industrial settings, corrosion-resistant stainless steel is often preferred, whereas residential spaces may utilize PVC for cost-effectiveness and ease of installation.
How to Select the Right Floor Drain for Different Applications?
Choosing the correct floor drain requires consideration of several factors, including water volume, drainage efficiency, installation type, and material durability. Floor drains are categorized based on load capacity, shape, and drainage mechanism. Circular and square grates are the most common designs, with perforated or slotted patterns to facilitate rapid water flow while preventing debris clogging.
Industrial spaces with heavy machinery require drains with higher load-bearing capacity and resistance to chemical corrosion. Residential bathrooms, on the other hand, prioritize ease of cleaning, odor prevention, and aesthetic integration with floor tiles. The height adjustment range is critical for accommodating variations in floor thickness or future renovations, ensuring that the drain remains flush with the surrounding floor surface.
Key considerations when selecting floor drains include:
-
Material Compatibility: Stainless steel for high moisture areas, PVC for lightweight, low-cost applications.
-
Flow Capacity: Adequate for expected water discharge; usually measured in liters per minute.
-
Odor Control: Incorporating anti-odor features such as water traps or silicone seals.
-
Maintenance Requirements: Removable grates and accessible trap systems facilitate easy cleaning.
-
Compliance with Standards: Ensuring load ratings and construction meet local plumbing codes.
By addressing these aspects, users can ensure optimal drainage performance and longevity while minimizing maintenance costs.
Common Questions About Floor Drains
Q1: What is the difference between a P-Trap and a Deep Seal Trap in floor drains?
A1: A P-Trap is a U-shaped pipe designed to retain a small water seal that prevents sewer gases from entering the building. Deep seal traps hold a larger water volume, offering enhanced odor prevention and protection against backflow. Deep seal traps are particularly suitable for areas with infrequent water flow, such as basements or storage rooms, whereas P-Traps are standard for residential bathrooms and kitchens.
Q2: How often should floor drains be cleaned and maintained?
A2: Floor drains should be inspected and cleaned at least once every three months to prevent clogging and odor accumulation. In high-traffic or industrial areas, monthly maintenance may be necessary. Cleaning involves removing debris from the grate, flushing water through the trap, and checking for signs of corrosion or leaks. Regular maintenance ensures continuous functionality and prolongs the drain’s lifespan.
How Do Floor Drains Contribute to Hygiene and Safety in Public and Private Facilities?
Floor drains play a pivotal role in maintaining hygiene by rapidly removing water, chemicals, and waste from floor surfaces. Accumulated water can lead to microbial growth, mold, and structural damage if not properly managed. In commercial kitchens, laboratories, or hospitals, efficient floor drainage is crucial for meeting sanitation regulations and preventing contamination.
Anti-slip grate designs reduce the risk of accidents caused by water accumulation. In industrial environments, drains must handle high-pressure cleaning operations and chemical residues. Features like removable strainers and chemical-resistant seals are essential to maintain operational safety and compliance with workplace health standards.
Beyond hygiene, floor drains facilitate flood prevention by efficiently channeling water from floors to the main sewer system. This capability minimizes property damage during heavy rainfall, plumbing failures, or accidental spills. Effective floor drainage systems, therefore, directly contribute to both the safety and the operational efficiency of facilities.
How Will Floor Drain Design Evolve with Emerging Construction Trends?
As construction and plumbing technology advance, floor drains are expected to incorporate smarter designs and higher durability standards. Innovations may include improved anti-odor systems, modular designs for rapid installation, and materials that combine corrosion resistance with environmental sustainability. In high-end residential and commercial buildings, aesthetic integration with flooring is becoming increasingly important, leading to customizable grates and low-profile designs.
Future trends also emphasize eco-friendly water management solutions. Floor drains may integrate with greywater recycling systems or smart sensors that monitor water levels and flow, alerting maintenance teams to potential blockages before they become critical. Such advancements align with the broader move toward sustainable construction practices and smarter facility management.
The role of advanced manufacturing techniques, such as precision casting and stainless steel polishing, ensures that floor drains meet high durability and performance standards. These developments promise longer service life, reduced maintenance costs, and better overall user experience.
In the context of modern water management, brands like Yanasi are recognized for combining durability, design, and efficiency. Their floor drains feature corrosion-resistant stainless steel, adjustable height options, and anti-odor traps, catering to both residential and industrial needs. For inquiries or to explore the full range of floor drain solutions, customers are encouraged to contact us directly for tailored guidance and support.